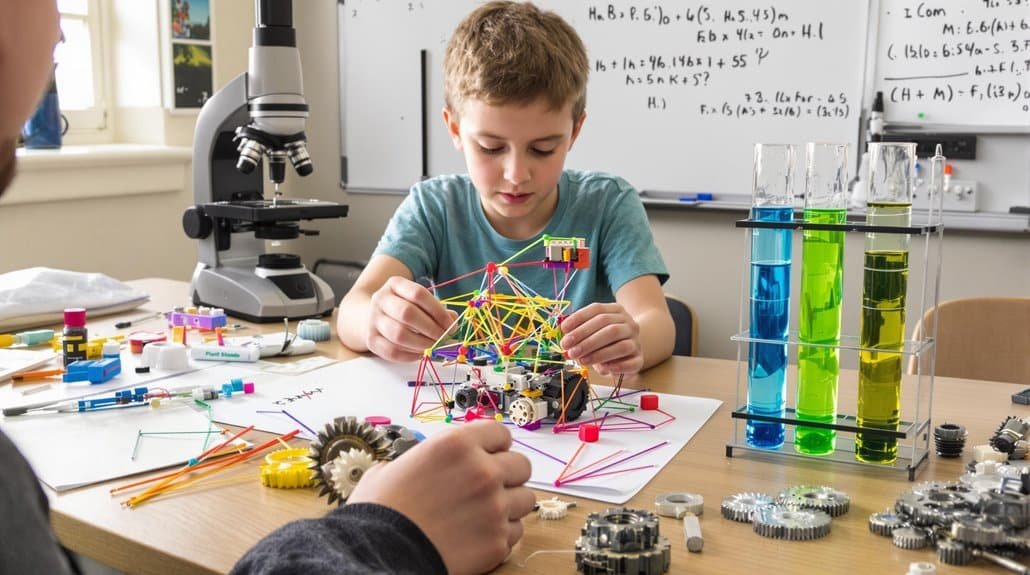
STEM learning integrates science, technology, engineering, and mathematics through hands-on projects that develop your child’s problem-solving abilities and scientific reasoning skills. Rather than teaching subjects in isolation, STEM education uses methodologies like the Engineering Design Process to create holistic learning experiences for children ages 5-16. Through robotics kits and visual programming platforms like Scratch, students build critical thinking skills while exploring real-world applications. This integrated approach prepares them for future careers where STEM professionals earn 30-40% more than their peers.
Core Components and Educational Methodology of STEM
When you explore STEM education for your child, you’ll discover that it represents far more than simply teaching science, technology, engineering, and mathematics as separate subjects.
Instead, STEM integrates these disciplines through structured methodologies like the Engineering Design Process and Scientific Inquiry Model, creating holistic learning experiences where collective knowledge surpasses individual components. Your child engages with driving questions that anchor project-based learning, promoting iterative problem-solving cycles. This interdisciplinary approach encourages critical thinking about real-world problems and applications that extend beyond traditional classroom boundaries.
This approach cultivates critical thinking and evidence-based reasoning through hands-on experimentation, preparing students aged 5-16 for college-level coursework while developing essential habits of mind for future STEM careers. Through professional development workshops, educators learn to incorporate quality STEM components that enhance lesson plans and improve student engagement with these integrated learning experiences.
Skills Development and Real-World Applications
As your child progresses through STEM education, they’ll develop critical competencies that extend far beyond academic achievement into practical workforce preparation.
Early engagement builds problem-solving abilities and scientific reasoning that become foundational for future success. Children who engage in STEM activities early develop positive attitudes toward science and are more likely to pursue STEM careers. Research shows STEM graduates earn approximately 40% higher salaries, with software development jobs projected to grow 17% by 2033.
STEM graduates earn 40% more while software development jobs surge 17% through 2033, creating unprecedented opportunities.
Key skills your child will develop include:
- Critical thinking and adaptive problem-solving
- Programming and computational reasoning
- Collaborative teamwork capabilities
- Scientific methodology and experimentation
- Creative engineering approaches
These competencies prepare students for emerging fields like AI, machine learning, and quantum computing technologies. Hands-on experience with robot kits provides practical application of these skills while fostering understanding of mechanics and electronics.
Benefits and Outcomes for Students and Society
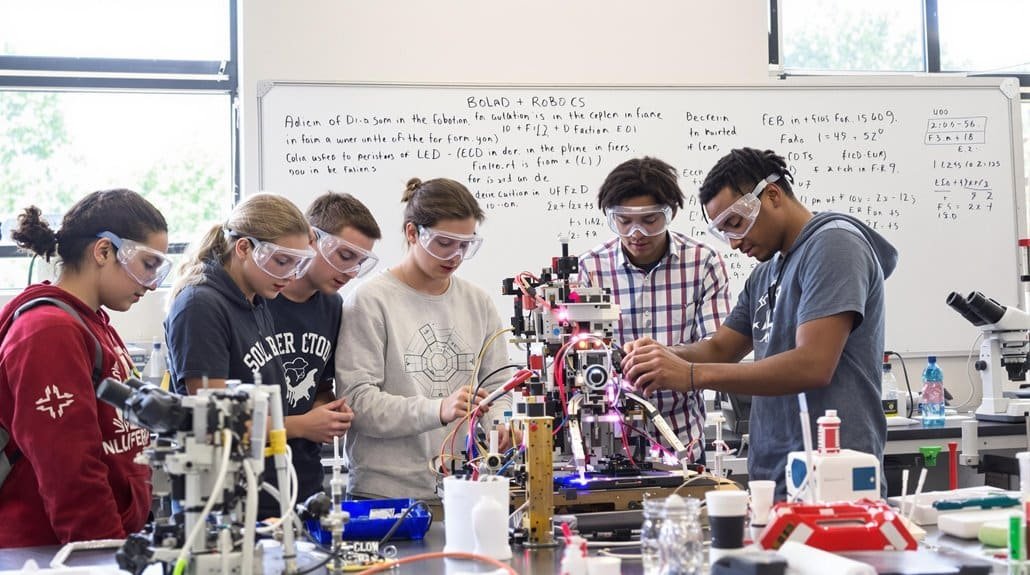

Beyond individual skill development, STEM education creates ripple effects that benefit both students and society through measurable economic and social outcomes.
You’ll find that students with STEM degrees earn 30-40% more than their peers, while these fields are growing nearly three times faster than non-STEM occupations. The demand for STEM professionals is projected to grow 8.8% from 2020 to 2030, creating abundant opportunities for prepared graduates.
For children ages 5-16, early exposure through robotics platforms and companion apps builds foundations for this economic advantage. Engaging with robotics education develops problem-solving and critical thinking skills through hands-on projects that promote troubleshooting and innovative solutions.
STEM programs also bridge socioeconomic gaps, providing equal opportunities for underserved communities.
Additionally, these educational pathways foster innovation and problem-solving capabilities essential for addressing tomorrow’s challenges, benefiting society through technological advancement and economic competitiveness.
Current Challenges and Future Innovations in STEM Education

While STEM education offers tremendous benefits, significant challenges threaten its effectiveness and accessibility across educational systems today.
You’ll find that current obstacles include:
- Only 16% of proficiency rates among students
- Gender disparities limiting female participation
- Insufficient teacher resources across schools
- Projected 2 million unfilled STEM positions
- International rankings showing U.S. students trailing
However, innovations like AI integration and mentorship scaling programs present promising solutions. The Department of Education has invested $540 million in STEM education to address these critical gaps in resources and support.
Educational systems are rapidly adapting curricula to incorporate emerging technologies, transforming how children aged 5-16 engage with STEM concepts through interactive platforms and companion apps that enhance learning outcomes. Visual programming platforms like Scratch coding are revolutionizing how students learn complex programming concepts by eliminating syntax barriers.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Age Should Children Start STEM Learning Programs?
You can start STEM learning programs when your child’s 3-5 years old, though informal exploration begins earlier. You’ll want to match activities to your child’s developmental stage, interests, and attention span for best results.
How Much Does STEM Education Typically Cost for Schools?
Your school likely spends around $217 per student annually on STEM education from a total budget exceeding $1 billion nationwide. Costs vary considerably based on equipment, teacher training, curriculum development, and facility requirements.
What Specific Certifications Do STEM Teachers Need?
You’ll need a bachelor’s degree, teaching license, and must pass certification exams. Many STEM-focused schools require additional STEM certifications covering science, technology, engineering, and math pedagogy. Subject-specific endorsements in areas like robotics may also be required.
How Do Parents Support STEM Learning at Home?
You’ll support STEM learning by creating hands-on exploration spaces, integrating science and math into daily activities like cooking, asking open-ended questions, celebrating achievements, and exposing children to diverse role models who inspire STEM confidence.
Which Countries Lead in STEM Education Implementation?
You’ll find Singapore and China topping STEM education rankings with PISA scores of 560 and 552 respectively. The US excels through premier institutions like MIT, while Germany and Switzerland dominate engineering and innovation infrastructure.
Conclusion
STEM learning equips your child with essential skills in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics through hands-on exploration. By integrating robotics toys and companion apps designed for ages 5-16, you’re fostering critical thinking, problem-solving, and technological literacy. These educational tools enhance cognition while providing engaging affordances that bridge theoretical concepts with practical applications. Investing in quality STEM resources today prepares your child for tomorrow’s innovation-driven careers, ensuring they develop competencies crucial for academic and professional success.