Understanding the Basics of Block Coding
Block coding is a beginner-friendly method to learn coding through a visual interface that replaces typed syntax with blocks of code. As a block-based coding language, it’s widely used in early coding classes and STEM programs to help kids and beginners get familiar with real coding concepts in a simple, interactive way.
Rather than writing text-based code, students build programs by dragging and stacking blocks that represent different code concepts. This drag and drop approach makes coding approachable, especially for those new to coding. Designed for beginners, it’s a great way to learn the basics of how programming works without overwhelming syntax.
Whether you’re trying to teach kids how to code at school or exploring a fun way for older kids or even adults to learn to code, block coding offers a structured but engaging introduction to coding fundamentals.
Popular Platforms That Use Block Coding
Many platforms support block coding for kids. Among them, Scratch, developed by the MIT Media Lab, stands out for its engaging, game-like experience that simplifies how kids can learn programming logic. By using Scratch, students can solve problems, create animations, and design interactive stories, all through snapping together visual coding blocks.
Google’s Blockly is another block-based programming tool that provides more flexibility for developers. While it shares similarities with Scratch, it’s more commonly integrated into educational platforms. For example, Code.org features a full coding curriculum powered by Blockly, where students can use block sequences to build projects and learn the basics of algorithms.
Thunkable is a block-based coding environment that allows users to build mobile apps visually. Platforms like Tynker and micro:bit offer curated lessons and block coding games that allow students to learn at their own pace, often with a progression into text-based coding languages like Python.
This kind of block coding experience makes it easy for kids to get involved in the world of coding. The extensive library of blocks these platforms offer means that kids can try different challenges and build their coding skills in a low-risk environment.
How Block Coding Facilitates Computational Thinking
One of the key educational benefits of block coding is its support for computational thinking, a foundational skill in both computer science and broader problem-solving disciplines. Block-based platforms help students learn to solve problems by breaking them into manageable steps, abstracting key elements, and applying structured logic.
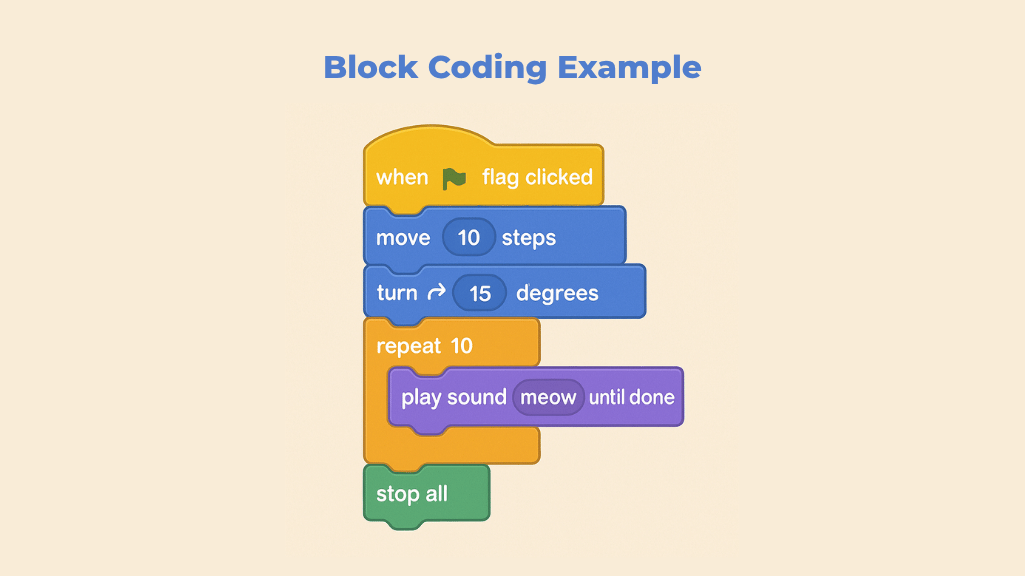
Visual blocks often include not just programming logic but also sound blocks, motion, and events, making learning interactive and accessible. For instance, using sound blocks in Scratch encourages students to make a computer react or behave in real-time, which reinforces concepts of coding and feedback loops.
Since block coding allows learners to focus on logical relationships without worrying about syntax, it provides a gateway for kids to learn core principles before transitioning into programming where text-based languages are used. This model of learning ensures that coding can be applied across various scenarios, from creating games to building basic apps.
Comparing Block-Based and Text-Based Programming
Traditional programming relies on text-based code, where each command must follow strict syntactic rules. While this allows for more power and flexibility, it can be intimidating for beginners. In contrast, block-based coding provides a more forgiving and structured way to explore programming logic.
The coding languages used in each method differ: block-based platforms like Scratch and Blockly are designed for ease of use, while text-based coding languages like Python or JavaScript require deeper understanding and typing skills. Still, coding involves the same foundational logic and structure across both types.
Transitioning from visual blocks to text allows learners to expand their coding experience, eventually using more advanced tools in real-world development.
Benefits and Limitations of Block Coding
Benefits
- Block coding allows learners to understand coding logic without syntax frustration.
- It makes it easy for kids to get excited about technology and start learning.
- Educators can teach coding through visuals, helping students learn iteratively.
- It allows kids to create, test, and improve projects in a playful, non-intimidating way.
Limitations
- As coding requires deeper abstraction for large projects, block-based languages may become limiting over time.
- Skills don’t always transfer directly to text-based coding languages, so guided transitions are key.
- Some users find that making coding projects beyond basic complexity is harder in a visual format.
Frequently Asked Questions
What age group is best suited for block coding?
Block coding is ideal for ages 6–14, but its structure is accessible enough that older kids, educators, and adult beginners can all benefit. The world of coding becomes less intimidating when logic is presented through drag and drop blocks.
How does block coding differ from regular coding?
Unlike traditional code, which uses text-based code, block coding relies on visual coding. It uses pre-built blocks to form programs, allowing learners to grasp code concepts and structure without the stress of syntax errors.
Can block coding prepare students for real-world programming?
Yes. While it simplifies syntax, it helps students internalize real coding concepts. Many tools now offer ways to shift from visual to text-based code, so coding can be applied to more advanced projects as learners grow.
Is block coding only for young learners?
No. While ideal for teaching coding to kids, it’s also used in coding classes for adult beginners, educators learning how to use modern tools, and non-programmers exploring automation.
What platforms use block-based coding?
Popular tools include Scratch, Blockly, Tynker, Thunkable, and Code.org. These platforms offer structured lessons, block coding games, and creative challenges, often including paths from visual learning to text-based coding languages.
Conclusion
Block coding is considered one of the most effective entry points into the world of coding. Its drag and drop system removes the friction of syntax, allowing students to learn through experimentation and visual logic.
As a visual coding method, it’s a great way for kids to learn, explore how computers work, and eventually transition to more advanced coding languages used in real-world environments. By bridging the gap between play and logic, it supports long-term development of coding fundamentals in a way that’s both scalable and inclusive.
If you’re ready to get started with block coding, platforms like Scratch, Tynker, and Code.org are great places to learn more about block coding and begin your coding experience. These tools are designed for beginners, support educators, and let students use them to build, share, and grow.
Ready to Take Block Coding to the Next Level?
If you’re looking to move beyond digital blocks and into real-world building, the Makeblock mBot Ranger Kit is an excellent next step. This 3-in-1 STEM robot lets kids code and control a tank, self-balancing robot, or racing car all using Scratch-based block programming.
It’s a hands-on way to apply what you’ve learned and bridge the gap between screen-based coding and physical robotics.